The burden of chronic diseases has increased over the last few decades, across all the geographies of the world, and the of patients (with chronic diseases) is estimated to rise in the future as well. As per a study, every six out of ten Americans are suffering from one or more chronic conditions, such as hypertension, diabetes, asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The complications of these diseases are reported to be the main cause of direct medical spending. For instance, in 2017, the economic burden for diabetes was reported to be USD 327 billion, in the US. It is worth highlighting that 60% of this cost was for inpatient care and medications to treat complications associated with diabetes, however only 15% share was spent on the medications to treat diabetes and other supplies, including glucometers and glucose test strips. Additionally, 13% of the total amount was spent on the physician office visits.
The increase in prevalence of chronic diseases and the requirement of repetitive drug administration to treat these conditions, are the major contributors to the growing demand for self-injection devices. Interestingly, the self-injection devices market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 22% and is likely to be valued at USD 80 billion by 2022. These days, number of patients are using these devices for administration of a variety of drugs, at their homes. Most of the growth in prefilled syringes market can be attributed to the increase in the number of patients using self-injection devices.
Moreover, traditionally, most of the pharmaceutical companies packaged their drugs and vaccines in conventional primary containers, such as glass vials. This was driven by expertise of both pharmaceutical companies and suppliers, garnered over several decades of use of such containers and related technology. Introduction of drugs in prefilled syringe format was a short term strategy of the companies for providing an optional form of drug administration to the patients / physicians. The mid-term strategy of companies included development of autoinjectors for their drugs, driven by the increase in preference for self-administration among patient population. Development of prefilled syringes and autoinjectors was used for life cycle management by the companies. However, considering the favorable adoption of prefilled syringes and ease-of-use, drug developers have started launching drugs in prefilled syringes, rather than in vials in order to differentiate themselves from the competitors. This trend will drive the use of prefilled syringes during the drug development stages, including different phases of clinical trials.
Further, prefilled syringes are also used in autoinjectors and pen-injectors. Various other factors, such as growth of the biosimilars market, growth in demand for vaccines, and the focus on preventing needlestick injuries, are likely to contribute to driving growth in the prefilled syringes market.
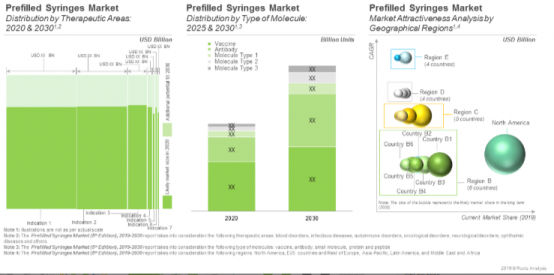
The prefilled syringes market is expected to witness a CAGR of nearly 4.2%; the opportunity is likely to be distributed across different therapeutic areas and geographical regions. The current prefilled syringes market is driven, to a large extent, by the syringes designed to deliver anticoagulants (54%), followed by delivery of vaccines (39%) for treatment of infectious diseases. Presently, Europe and North America hold the major share (48%) in the prefilled syringes market, followed by Asia-Pacific (such as China, Japan and India) that capture 9% of the opportunity in 2020. Interestingly, market in Middle East and Africa is likely to grow at a relatively faster pace in future.
The ‘Prefilled Syringes Market (5th edition), 2019-2030’ report features an extensive study of the current market landscape of prefilled syringes and the likely future opportunities associated with such devices, over the next 10-12 years. It features an in-depth analysis, highlighting the capabilities of various stakeholders engaged in this domain.