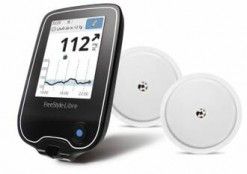
Check your blood glucose level without finger pricks using Continuous Glucose Monitor, a glucose monitoring system that includes sensors to scan your blood sugar
A blood glucose meter must be adapted to the needs of each patient. Before purchasing it, it is therefore necessary to consider several factors such as ease of handling and transport, the units of measurement displayed or the use of the chip (code).
User-friendliness: The user interface of the Continuous Blood Glucose Monitoring System must be intuitive and display the results and their description in an easily understandable way. Some models have a comfortable and easy to use touch screen. The device should preferably be of a size and shape with a good grip.
Easy to carry: since the patient must be able to measure his blood glucose level anywhere and at any time of the day, easy carrying is a crucial point. The patient will therefore be more inclined to choose a light and space-saving model. Weight should not be a limitation, especially for young patients.
Units of measurement of blood glucose: Depending on the meter, the results can be given in g/l, mg/dl or mmol/l. This can confuse the diabetic if he or she does not pay attention to the unit of measurement selected Continuous Blood Glucose Monitoring System (for meters with multiple device options). The conversion from mg/dl to g/l is obtained by dividing the value obtained by 100. For example, if the meter is set in mg/dl and displays a result of 123, this means that the patient has a capillary blood glucose level of 1.23 g/l. The conversion from mmol/l to g/l is obtained by multiplying the mmol/l value by 0.18.
Use of the chip (code): With some blood glucose meters, each box of test strips contains a specific chip that must be used and disposed of after use. Poor matching of the reader and test strip may result in incorrect values, therefore Continuous Blood Glucose Monitoring System is specially For all blood glucose readers that require this adjustment, it is important to ensure that the code displayed on the meter matches the code printed on the test strip vial used before each test. If this is not the case, no measurement should be performed. However, there are models where entering the code is not necessary to ensure the quality of the results.
Which measuring principle does a blood sugar measuring device use?
There are currently several measurement technologies on the market. They are mainly electrochemical (enzymatic) and can be divided into three categories:
Using glucose oxidase
With glucose dehydrogenase
By means of glucose-dye-oxidoreductase.
The results obtained may vary depending on the technology used. It is therefore always very important to use Continuous Blood Glucose Monitoring System test strips that are compatible with the technology indicated on the meter.
These technologies may also interfere with some patients' treatments. For example, glucose oxidase readers interfere with oxygen therapy. The use of Glucose Dye Oxidoreductase interferes with maltose and galactose and polysaccharides or oligosaccharides in infusion solutions. Maltose may be present in high concentrations in the blood, either directly (immunoglobulin preparations) or after metabolization (example of ixoderin used for peritoneal dialysis).
The risk of overestimating blood sugar levels is therefore very high and should not be considered lightly. Very often there are indications of the blood glucose monitoring devices affected by this type of interaction, such as the prohibition to use the device in the case of peritoneal dialysis.
Continuous Blood Glucose Monitoring System is one of the best options for all blood test and diabetes patients they can take this device anywhere and can use anytime without any pain, as it is Pain-Free Blood Glucose Monitoring System, so no need to be worry about finger prick again and again.